Older Patient Outcomes
Research is showing that older chronological age per se is not a contraindication for hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT), especially in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
The number of hematopoietic cell transplants in older patients has grown in the last decade due to the use of reduced-intensity and non-myeloablative conditioning regimens, which use lower doses of chemotherapy and/or radiation. These less-intense regimens rely on immunosuppression to permit engraftment in the patient, and it is the donated allo-reactive T cells that then eradicate residual malignant cells through a graft-versus-tumor effect.
View the video below for the latest research affecting treatment decisions for older patients with AML who are considering HCT.
Due to advances in treatment such as reduced-intensity conditioning regimens, the number of older patients receiving a blood stem cell transplant has increased significantly in recent years. In 2022, Be The Match® facilitated 3,895 transplants for patients over age 50. That represents 58% of 2022 transplants.
Advances
The use of less intense pre-transplant conditioning regimens, along with progress in post-transplant care, have allowed more patients >50 years or those with co-morbidities to undergo allogeneic HCT. Recent research has demonstrated that:
- Chronological age per se should not serve as a barrier to transplant [2-5]
- Reduced-intensity HCT using HLA-matched unrelated donors is feasible and effective in older patients with AML in CR1 [6]
- Reduced-intensity HCT using HLA-matched unrelated and unrelated donors is feasible and effective in older patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in CR1 [7]
- Older patients can achieve comparable quality of life when compared with younger patients [8]
Outcomes
Outcome data in this section have been prepared by CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research), our research program.
Figure 2. MDS Survival, Unrelated HCT, by Age
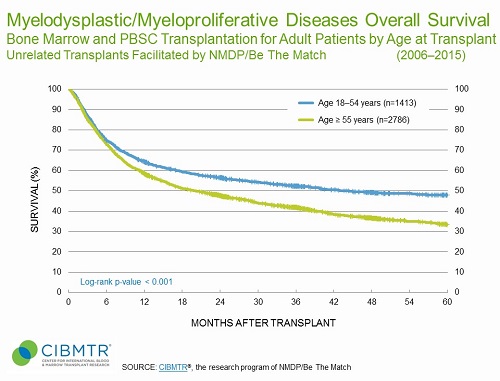
Figure 3. AML Survival, Unrelated HCT, Patients ≥55 years

References
- NMDP 2017 Fiscal Year Reports.
- Rashidi A, Ebadi E, Colditz GA, DiPersio JF. Outcomes of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22(4): 651-657. Access
- Atallah E, Horowitz MM, Logan B, et al. Outcome of patients 65 years and older with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) receiving allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation compared to patients 55-64 years of age (abstract). Blood. 2015; 126(23): 193. Access
- McClune BL, Weisdorf DJ, Pedersen TL, et al. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28(11): 1878-1887. Access
- Reshef R, Porter DL. Reduced-intensity conditioned allogeneic SCT in adults with AML. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015; 50(6): 759-769. Access
- Devine SM, Owzar K, Blum W, et al. Phase II study of allogeneic transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission using a reduced-intensity conditioning regimen: Results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network 0502. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33(35): 4167-4175. Access
- Rosko AE, Wang H-L, de Lima M, et al. Reduced-intensity conditioned allograft yields favorable survival for older adults with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2017; 92(1): 42-49. Access
- Hamilton BK, Rybicki L, Dabney J, et al. Quality of life and outcomes in patients ≥60 years of age after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014; 49(11): 1426-1431. Access