Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
Approximately 8,900 individuals in the United States are diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) each year. This myeloproliferative neoplasm primarily affects older adults, with a median age at diagnosis of 65 years. Approximately 2% of patients diagnosed with CML are under the age of 20. [1]
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is no longer considered first-line treatment for adults with CML due to evidence of significant clinical benefit for patients receiving BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs).
Allogeneic HCT is indicated for patients with CML who have an inadequate hematologic or cytogenetic response. [2] HCT is also for CML patients whose disease develops resistance to TKI treatment or those intolerant to TKIs and remains the only curative option. [3-5]
Outcomes
Data in this section have been prepared by the CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research®). The CIBMTR is a research collaboration between the National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the Medical College of Wisconsin.
Figure 1. CML Survival, Matched Related and Matched Unrelated HCT
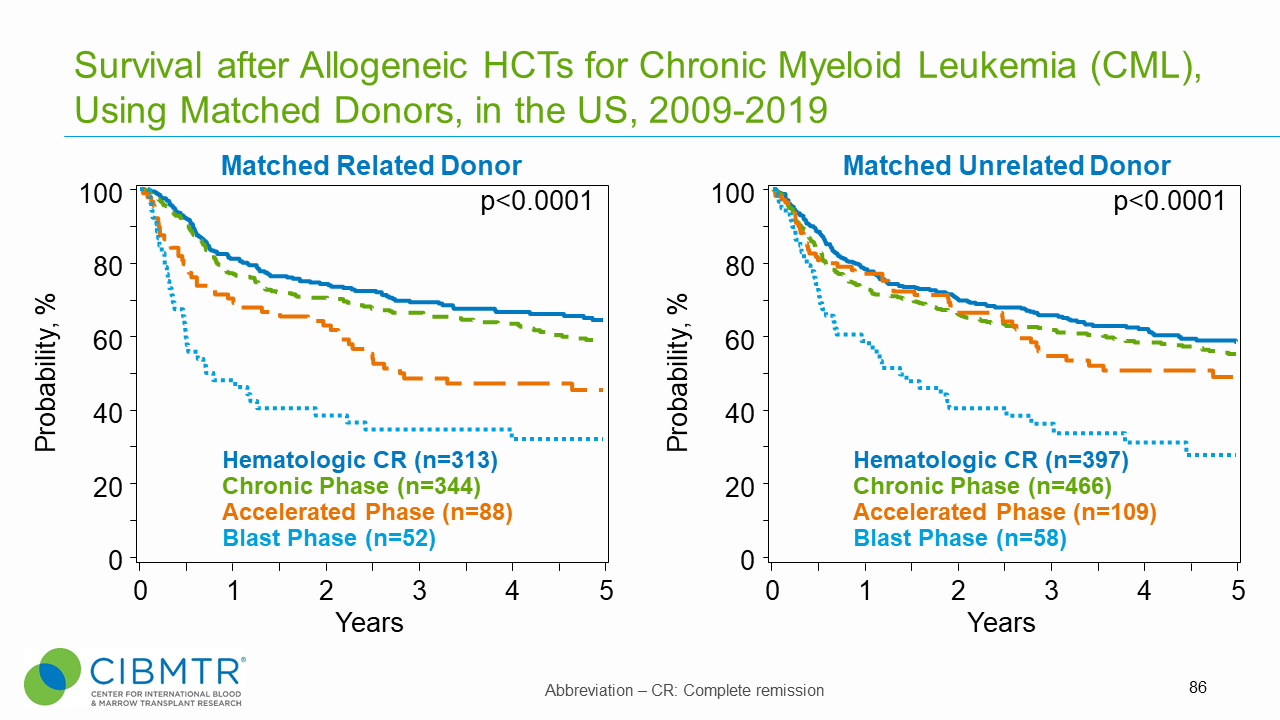
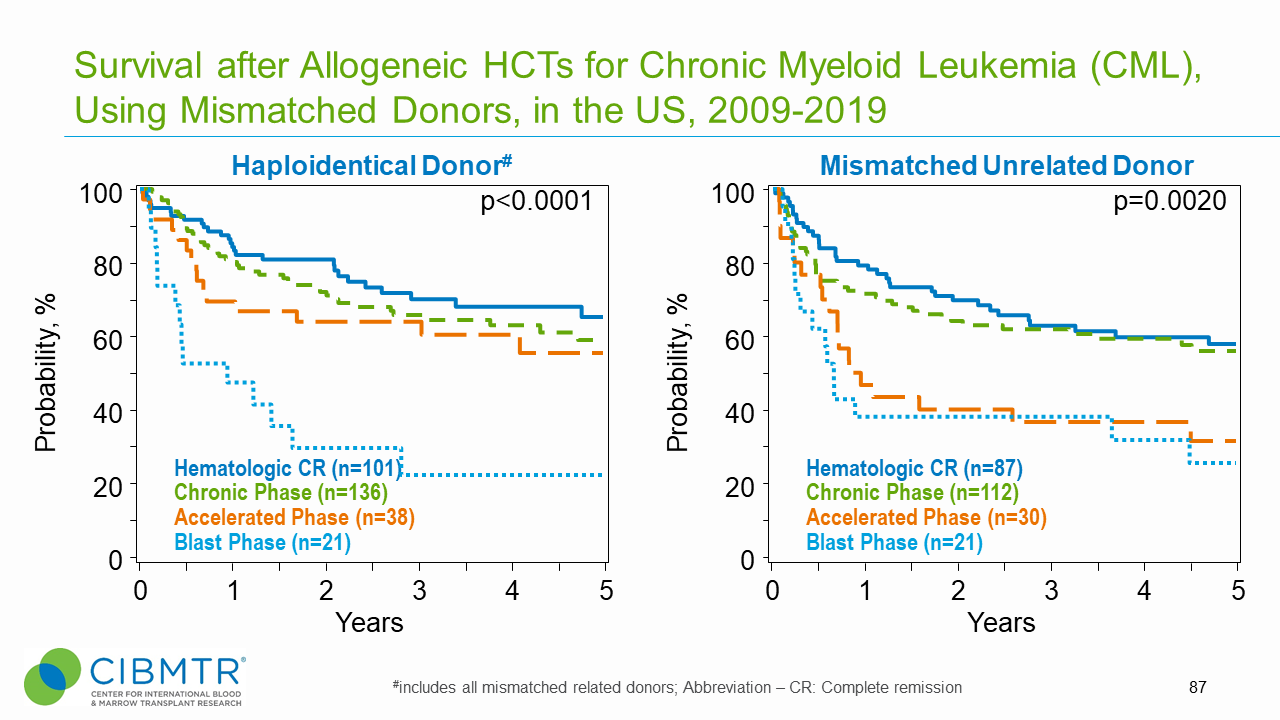
Figure 2. CML Survival, Haploidentical and Mismatched Unrelated HCT
HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
The National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) have jointly developed guidelines for transplant consultation and referral timing based on disease characteristics. [2] The National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines (NCCN Guidelines®) were consulted when developing these guidelines and are a valuable tool in determining risk stratification. [6]
Our guidelines highlight disease categories that include patients at risk for disease progression and who should be referred for a consultation for autologous or allogeneic transplantation. [2]
Transplant Consultation Guidelines: CML
- Inadequate hematologic or cytogenetic/molecular response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapies
- Disease progression
- Intolerance to TKI therapies
- Accelerated phase
- Blast crisis (myeloid or lymphoid)
- T315I mutation
View complete HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
Clinical Trials Search and Support
The NMDP/Be The Match offers the Be The Match® Jason Carter Clinical Trials Search and Support (CTSS) program, which can provide clinical trial navigation to your patients. The CTSS Program was created to help people with blood cancers or blood disorders and their families find and join clinical trials.
For more information, visit Clinical Trials Search and Support.
References
- SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Website accessed 2 November, 2017. Access
- NMDP/Be The Match and ASTCT Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation. Download (PDF)
- Warlick E, Ahn KW, Pedersen TL, et al. Reduced intensity conditioning is superior to nonmyeloablative conditioning for older chronic myelogenous leukemia patients undergoing hematopoietic cell transplant during the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era. Blood. 2012; 119(17): 4083-4090. Access
- Jabbour E, Cortes J, Santos FPS, et al. Results of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia patients who failed tyrosine kinase inhibitors after developing BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutations. Blood. 2011; 117(13): 3641-3647. Access
- Velev N, Cortes J, Champlin R, et al. Stem cell transplantation for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia resistant to tyrosine kinase inhibitors with BCR-ABL kinase domain mutation T315I. Cancer. 2010; 116(15): 3631-3637. Access
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. (Version 1.2023). Access