Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) affects approximately 100,000 Americans and occurs in about 1 out of every 365 African American births. [1]
This hemoglobinopathy is primarily found in individuals with African, Mediterranean, South American, Southeast Asian, and Middle Eastern lineages. SCD leads to lifelong morbidity and reduced life expectancy through end-organ damage.
Although supportive care, drug therapies, and red blood cell transfusions can ease symptoms and extend lifespan, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is the only established potential cure for SCD. [2-7] The 10-year survival for patients who survive at least two years after HCT was 96% in a recent analysis.[2]
Outcomes
Data in this section have been prepared by the CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research®). The CIBMTR is a research collaboration between the National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the Medical College of Wisconsin.
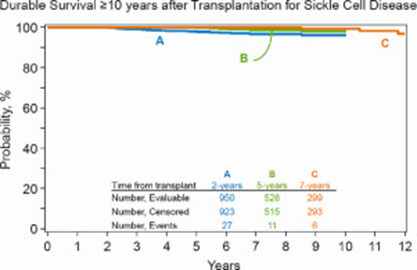
Figure 1. Pediatric Survival after Allogeneic HCT for SCD
Figure 2: Pediatric SCD Survival, Unrelated HCT
HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
The National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) have jointly developed guidelines for transplant consultation and referral timing based on disease characteristics. [9] The National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines (NCCN Guidelines®) were consulted in developing these guidelines and are a valuable tool in determining risk stratification. [10]
Our guidelines highlight disease categories that include patients at risk for disease progression and who should be referred for a consultation for hematopoietic cell transplantation. [9]
Transplant Consultation Guidelines: Hemoglobinopathies
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD)
Children with available matched sibling donor should be referred at diagnosis
- All patients with aggressive course (stroke, end-organ complications, frequent pain crises)
- All patients with an alternative donor option and any of the following:
- Stroke or silent cerebral infarct or cognitive impairment >24 hours
- ≥2 episodes of acute chest syndrome/2-year period [or] ‘recurrent’ acute chest syndrome
- Regular red blood cell transfusion therapy (8 or more per year)
- Tricuspid value regurgitant jet (TRJ) velocity ≥2.7 m/sec
- Chronic pain ≥6 months (leg ulcers, avascular necrosis)
- Abnormal transcranial Doppler (TCD) velocity of ≥200 cm/sec or >185 cm/sec with intracranial vasculopathy
- Silent cerebral infarct
- ≥3 severe vaso-occlusive pain crises per 2-year period
View complete HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
Clinical Trials Search and Support
The NMDP/Be The Match offers the Be The Match® Jason Carter Clinical Trials Search and Support (CTSS) program, which can provide clinical trial navigation to your patients. The CTSS Program was created to help people with blood cancers or blood disorders and their families find and join clinical trials.
For more information, visit Clinical Trials Search and Support.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Sickle Cell Disease, Data and Statistics; accessed 13 January, 2018. Access
- St. Martin, A. et al. Long-term survival after hematopoietic cell transplant for sickle cell disease compared to the United States population. Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. 2022; 28(6): 325.e1–325.e7. Access
- Walters MC, De Castro LM, Sullivan KM, et al. Indications and results of HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic cell transplantation for sickle cell disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22(2): 207-211. Access
- Saraf SL, Oh AL, Patel PR, et al. Nonmyeloablative stem cell transplantation with alemtuzumab/low-dose irradiation to cure and improve the quality of life of adults with sickle cell disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22(3): 441-448. Access
- Bhatia M, Jin Z, Baker C, et al. Reduced toxicity, myeloablative conditioning with BU, fludarabine, alemtuzumab and SCT from sibling donors in children with sickle cell disease. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014; 49(7): 913-920. Access
- King AA, Kamani N, Bunin N, et al. Successful matched sibling donor marrow transplantation following reduced intensity conditioning in children with hemoglobinopathies. Am J Hematol. 2015; 90(12): 1093-1098. Access
- Lucarelli G, Isgrò A, Sodani P, et al. Hematopoietic SCT for the Black African and non-Black African variants of sickle cell anemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014; 49(11): 1376-1381. Access
- Gluckman E, Cappelli B, Bernaudin F, et al. Sickle cell disease: an international survey of results of HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2017; 129(11): 1548-1556. Access
- NMDP/Be The Match and ASTCT Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation. Download (PDF)
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCC Guidelines. 2023. Access