Severe Aplastic Anemia and Other Marrow Failure Syndromes
Acquired aplastic anemia is thought to have an autoimmune component in many patients, and immunosuppressive therapy is a typical frontline therapy. Patients with aplastic anemia are classified based on the severity of their marrow aplasia. Those with severe aplastic anemia (SAA) are candidates for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). [1-4]
Bone marrow failure syndromes are rare diseases with abnormal or absent hematopoiesis in one or more cell lines. They include acquired or congenital aplastic anemia, Fanconi anemia and Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Most patients are diagnosed in childhood and commonly present with hematologic findings such as single-cell or pancytopenia, myelodysplastic syndromes or leukemia, particularly acute myeloid leukemia. [1]
Diamond-Blackfan and Fanconi anemia are rare heterogeneous disorders characterized by red cell aplasia. Many patients eventually develop pancytopenias from these syndromes. Allogeneic HCT offers the only potential cure for both disorders. [1,4] A 2016 study of long-term survival in patients transplanted for Fanconi anemia found that 10 and 15-year probabilities of survival were 90% and 79%, respectively. [5]
Outcomes
Outcome data in this section have been prepared by the CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research®). The CIBMTR is a research collaboration between the National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the Medical College of Wisconsin.
Figure 1: SAA Survival, Adult and Pediatric HCT
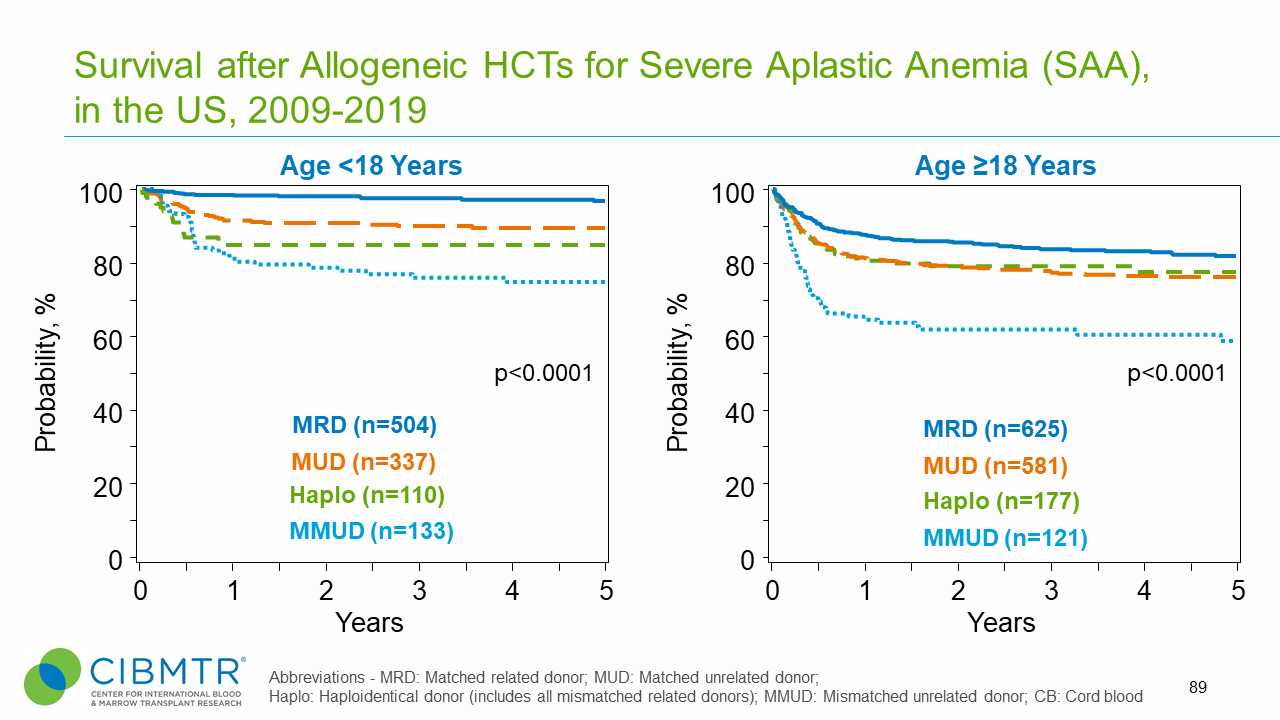
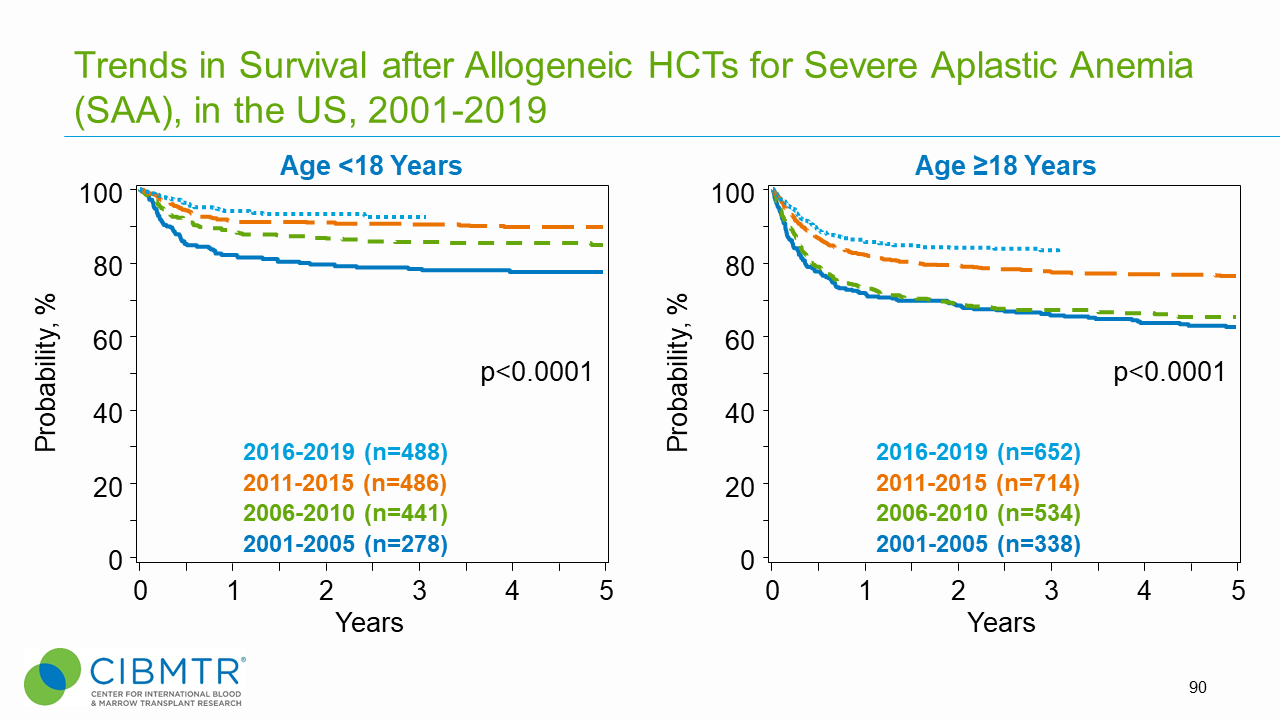
Figure 2: SAA Survival Over Time, Adult and Pediatric HCT
HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
The National Marrow Donor Program® (NMDP)/Be The Match® and the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) have jointly developed guidelines for transplant consultation and referral timing based on disease characteristics. [6] The National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Practice Guidelines (NCCN Guidelines®) were consulted in developing these guidelines and are a valuable tool in determining risk stratification. [7]
Our guidelines highlight disease categories that include patients at risk for disease progression and who should be referred for a consultation for transplantation.[6]
Transplant Consultation Guidelines: Severe Aplastic Anemia and Other Marrow Failure Syndromes
Including Fanconi anemia, Diamond-Blackfan anemia, Shwachman-Diamond syndrome, and others
- At diagnosis
View complete HCT Consultation Timing Guidelines
Clinical Trials Search and Support
The NMDP/Be The Match offers the Be The Match® Jason Carter Clinical Trials Search and Support (CTSS) program, which can provide clinical trial navigation to your patients. The CTSS Program was created to help people with blood cancers or blood disorders and their families find and join clinical trials.
For more information, visit Clinical Trials Search and Support.
References
- Alter BP. Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes: considerations pre- and posttransplant. Blood. 2017; 130(21): 2257-2264. Access
- Tolar J, Sodani P, Symons H. Alternative donor transplant of benign primary hematologic disorders. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2015; 50(5): 619-627. Access
- Scheinberg P, Young NS. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2012; 120(6): 1185-1196. Access
- Smith AR, Wagner JE. Current clinical management of Fanconi anemia. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012; 5(5): 513-522. Access
- Bonfim C, Ribeiro L, Nichele S, et al. Long-term survival, organ function, and malignancy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for Fanconi anemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22(7): 1257-1263. Access
- NMDP/Be The Match and ASTCT Recommended Timing for Transplant Consultation. Download (PDF)
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Guidelines. 2023. Access